Architecture
wasmCloud's Elixir host runtime has been deprecated. The Rust wasmCloud runtime is receiving all new features
The following diagram illustrates the composition of the Elixir OTP host:
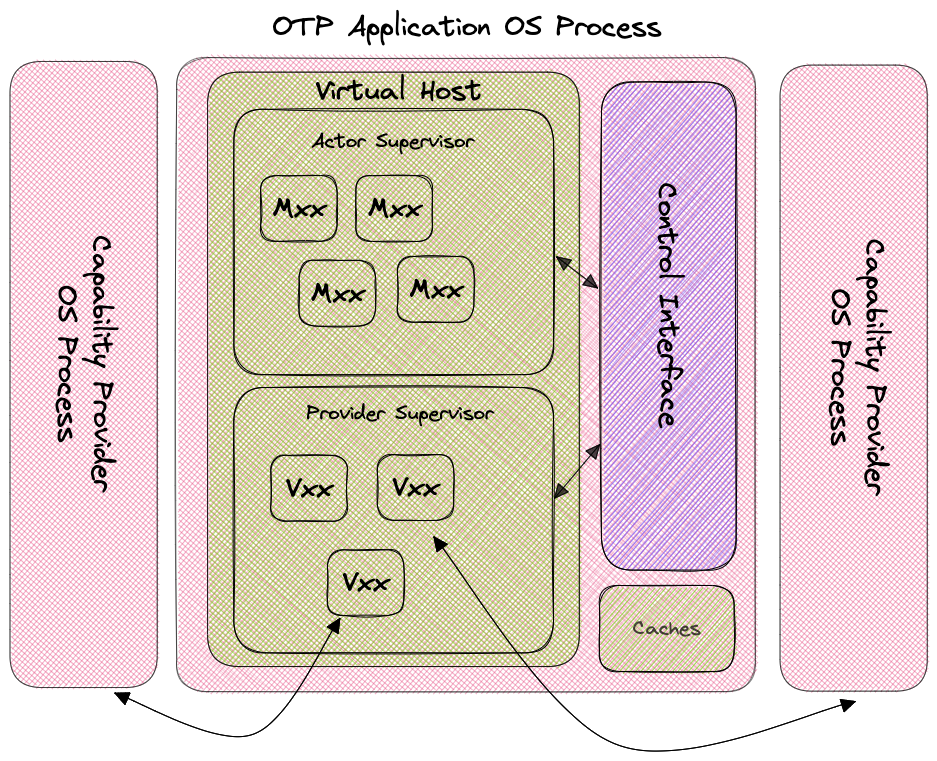
In this diagram, Mxxx represents an actor (an actor's public key is a 56-character string starting with M) while Vxxx represents a capability provider (their public keys start with V).
The unit of deployment is the single OTP application. See the GitHub repository for details and specifics of how this application is deployed, including instructions for use with Docker.
Inside each deployed Elixir wasmCloud host, there is a process supervisor called the Virtual Host. Beneath this supervisor are two more supervisors: the Actor Supervisor and the Provider Supervisor. In turn, each of these supervise individual processes for actors and providers.
The actor process contains a NIF-based instance of the Rust runtime responsible for loading and managing WebAssembly modules and components.
The capability provider process is a bit tricky. It uses an Elixir Port to spawn a new operating system process for the capability provider binary (which is extracted from a provider archive file) suitable for the current operating system and CPU architecture.
The blanket term wasmCloud Host refers to the combination of the core Elixir OTP operating system process and all of the OS processes spawned for capability providers.
If a host is asked to gracefully terminate, then it will usually be able to stop all of the capability provider OS processes. However, sometimes that doesn't work or other times (like when you're developing locally), the host may be terminated forcefully. This can orphan capability providers. To find them and terminate them, locate them with the following shell command (or your OS equivalent):
ps -ef | grep wasmcloud
Also, if you find that you may have orphaned the actual OTP host and not just a provider, you can look for the beam process:
ps -ef | grep beam
We all look forward to the bright future when we might be able to replace provider archive files containing OS/CPU-bound binaries with fully portable WASI components. Until then, spawning an OS process for a capability provider is the only way to manage them.